Introduction digital.transformation Radar
„Digital Transformation“ is a buzz word that is understood in very different ways. We have therefore clarified the terminology for the scope of any strategic Project within an entity, division of any Insurance Group.
It is important to understand that this journey may vary greatly within any group. A shared business understanding must thus be established of what digital transformation should entail in the specific strategic context of an entity or a business unit rsp Group.
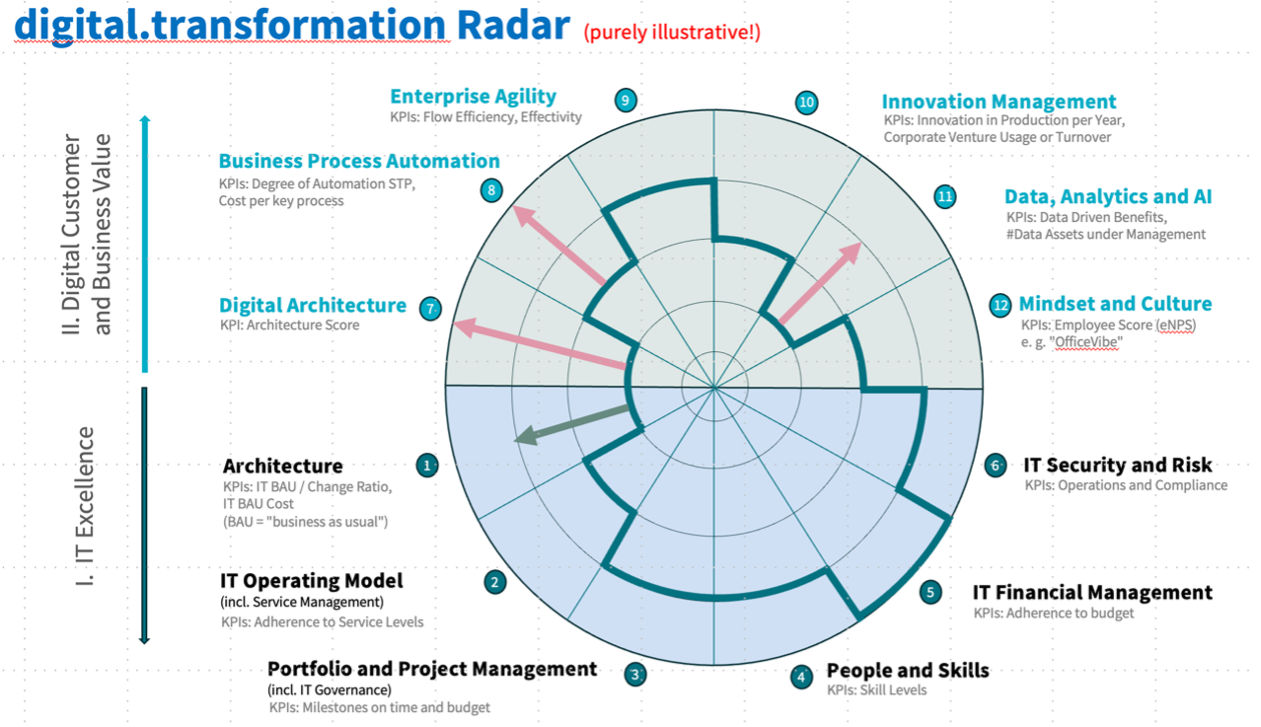
The digital.transformation Radar serves this purpose. It describes the existing digital capabilities of each entity as well as of the group, as surveyed in phase 1 of the project, and, resulting from the upcoming phase 2 of the project, the respective ambitions proposed by the project team for inclusion in a respective business strategy project.
The two main perspectives of the Radar:
I. IT Excellence
II. Digital Customer and Business Value
the surveyed twelve digital capabilities:
1. Architecture
2. IT Operating Model
3. Program and Project Management
4. People and Skills
5. IT Financial Management
6. IT Security and Risk
7. Digital Architecture
8. Business Process Automation
9. Enterprise Agility
10. Innovation Management
11. Data, Analytics and AI
12. Mindset and Culture
the maturity levels, and how the digital.transformation Radar can be used are explained on the following pages.
A. The Two Main Perspectives
- IT Excellence: The lower segment of the circle displays six capabilities grouped into the cluster „IT Excellence“. IT Excellence describes the „machine room“ and capabilities that are needed to make best use of the machine room. In this cluster, „IT“ must (and can) largely take the lead itself to increase maturity.
- Digital Customer and Business Value: The upper segment „Digital Customer and Business Value“ is a combined shortform for „Digital Customer Value“ plus „Digital Business Value“. It names six capabilities that relate to the value created by the division, when applying two viewpoints: a customer-oriented viewpoint and a broader business-viewpoint. Here, a co-creation approach is needed. Neither IT nor business can be successful on their own.
- Customers: The capabilities in the upper segment increase the relevance to the customer. Examples for ways to increase the customer value are instant new features in a Customer Journey (evidence of the company’s ability to respond to what the customer needs), the ability to faster process PDF uploads from a customer thanks to reliable Optical Character Recognition (OCR) or to create interactions that permit a more relevant personalized interaction with the customer (individual, password-protected online space on the company site where the customer not only finds relevant information but also can exchange with the company in a dedicated way). Automation is an important capability in all three examples, as it helps to implement the central credo of „providing customer value faster„.
- Business: When applying the broader, business-oriented perspective, the question is: „How does value creation to the customer, alongside with other measures owed to digitalization, translate into an increase of business value?“ A focus on business leads to the question on how the shareholder value can be increased. Examples for ways to increase the business value are activities leading to lower costs of processes and interactions, to an elimination of unnecessary steps in a process (waste), to the avoidance of consumptions that are unnecessary (waste), or to an increase of the profit margin attributable to an identified product.
B. The maturity levels
A maturity degree between 1 and 5 (5 being a stretched target state/north star that only few digital companies might have reached today).
However, when an entity has reached the maximum score (5 / 5) the mission is not completed. A higher ranking than what is shown on the digital.transformation Radar is possible.
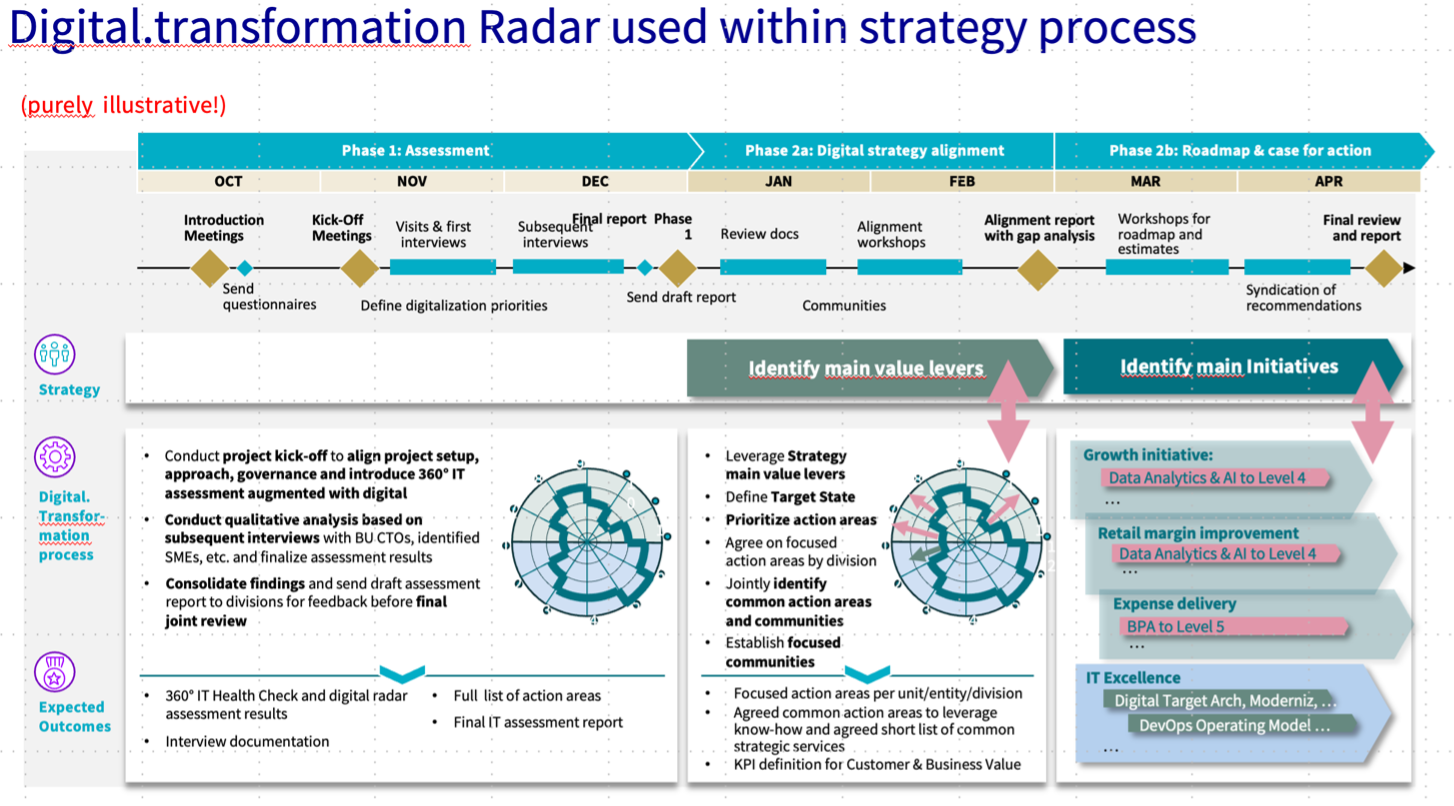
C. How to use the digital.transformation Radar – within a project and beyond
Primary purpose of the digital.transformation Radar is to demonstrate maturity of an entity or divi-sion. The digital.transformation Radar shall be used to articulate focus and ambition level, as well as development of maturity level. (The digital.transformation Radar shows arrows to indicate that strategic initiatives can be defined in phase 2b.)
Assessment (Phase 1): The digital.transformation Radar shows the results of a entity/division’s self-assessment, as well as of Group IT. The project team shall challenge the maturity assessment.
Digital Strategy Alignment (Phase 2a): The digital.transformation Radar will be the starting point to discuss in which area an entity rsp division should increase its maturity level. At least one KPI should be defined for a selected focus area to enable a fact-based strategic conversation.
Roadmap and Case for action (Phase 2b): A focus area in which a division wants to improve can be integrated into the entity/divisional or group strategy, so permitting focused investments and an increase of business value. For all initiatives should identify expected benefits, interdependencies, and risks. This will make it possible to aggregate initiatives at entity/divisional or group level, in case this seems useful.

Erfahrung & Expertise
Die digital advisor der bluerock27 ag haben über 20 Jahre Erfahrung in den Bereichen Technologie, Daten und Innovations Management bei grossen Versicherungsfirmen in der Schweiz und weltweit.
Unsere Erfahrung und Expertise stellen wir gerne unseren Kund*innen zur Verfügung und freuen uns darauf die digitale Zukunft gemeinsam mit Ihnen zu gestalten.
– Andreas Maier